Oxygen concentrators are devices used to produce high-purity oxygen from atmospheric air. They are widely used both at home and in medical facilities—in oxygen therapy supporting the treatment of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, as well as in conditions of hypoxia. Depending on their purpose, concentrators can be designed as portable individual devices or as stationary installations, supplying oxygen to multiple users simultaneously.
Their operation is based on Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA/VPSA) technology, which involves the cyclic separation of air components using molecular sieves—specialized zeolite adsorbents. These sieves selectively capture nitrogen during compression, allowing the remaining stream to be enriched with oxygen. During decompression, the adsorbed nitrogen is desorbed back into the environment, and the cycle repeats. This process does not chemically wear the adsorbent, allowing for its repeated use.
In oxygen concentrators, two types of molecular sieves are most commonly used:
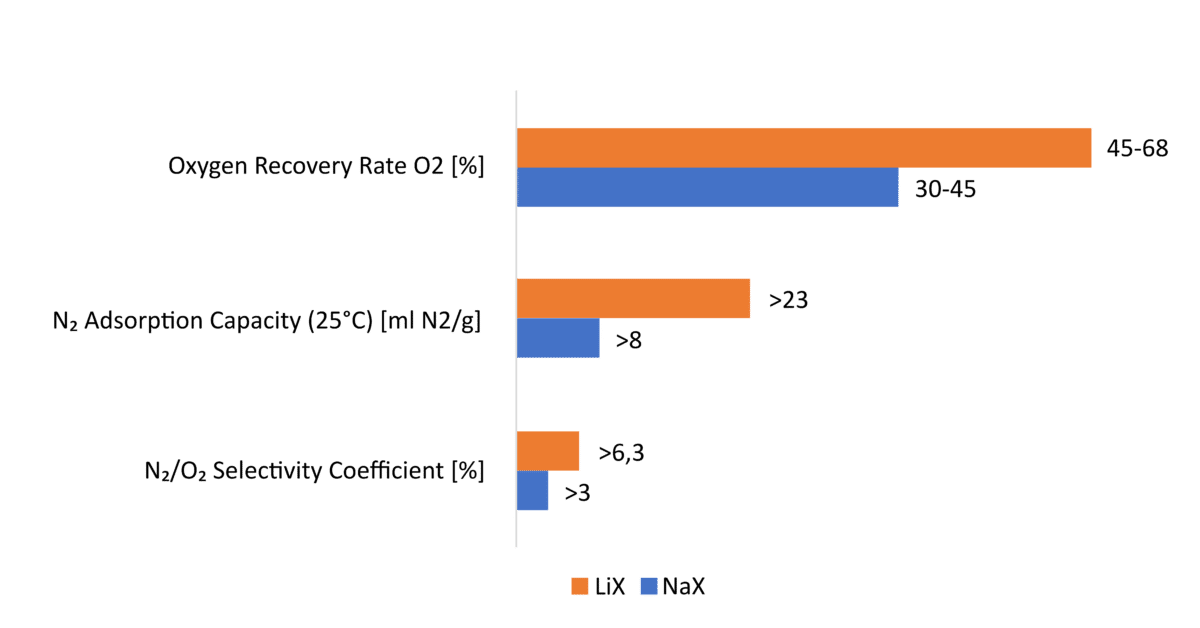
- LiX (lithium zeolite type X) – characterized by higher selectivity for nitrogen and shorter cycle times. This enables greater oxygen efficiency at lower energy consumption, making them the preferred choice in modern, compact medical concentrators.
- NaX (sodium zeolite type X) – known for good stability and lower cost, they are often used in older devices or less demanding applications where economic operation is a priority.
The choice of sieve type depends on the concentrator’s design and user requirements—from portable devices with low power consumption to high-efficiency stationary installations.